# Vue 2.x 源码解析
Vue (读音 /vjuː/,类似于 view)是一套用于构建用户界面的渐进式框架。
渐进式:可以在已有的系统中部分页面先使用Vue,先只使用Vue的部分功能,然后再慢慢扩展Vue的全家桶
在 Vue 应用中,组件的依赖是在渲染过程中自动追踪的,所以系统能精确知晓哪个组件确实需要被重渲染。你可以理解为每一个组件都已经自动获得了 shouldComponentUpdate。
Vue 运行:
- 在创建时(beforeCreate之后created之前)使用依赖收集实现双向绑定
- render不存在的时候会去编译template(即支持 render写法 也支持 template写法)
- template编译会被解析成对象形式的树结构(抽象语法树(abstract syntax tree或者缩写为AST))
- AST会经过generate得到render函数,render的返回值是VNode,也就是虚拟DOM
- 虚拟Dom的在更新时会经过 setter -> Dep -> Watcher -> update -> patch。
- patch的核心时diff算法(通过同层的树节点进行比较),会涉及sameVnode的概念
Vue 主要模块:
- 四个事件($on,$once,$off,$emit)实现方式类似EventBus
- 生命周期(创建,挂载,更新,销毁)
- nextTick (有多种降级策略)
- keep-alive 和 instance(基于VNode节点),还有activated与deactivated
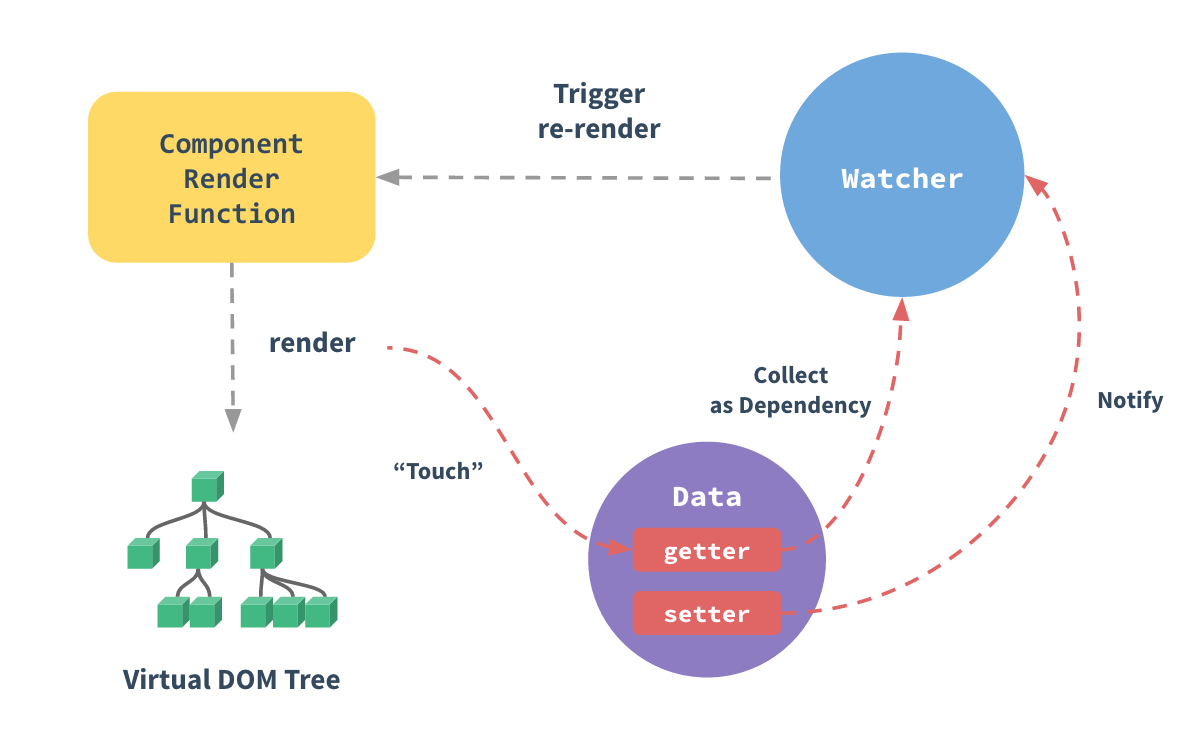
# 实现双向绑定
Vue的双向绑定是
利用订阅-发布者模式+数据劫持实现的
利用Object.defineProperty的getter方法:由Deps收集Watcher对象,在setter中notify。
在getter中实现绑定的而不是setter,这样可以只劫持被使用的数据。
双向绑定实现原理图:
实现一个简单的双向绑定:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div>
<input v-model="num"/>
<p v-bind="num"></p>
</div>
<div>
<button @click="addNum">
加一次
</button>
</div>
</div>
<script>
let protoToString = Object.prototype.toString;
function isArray(value) {
return protoToString.call(value) === '[object Array]'
}
class Watcher {
constructor(node, cb, key){
this.node = node;
this.cb = cb;
this.key = key;
}
update () {
this.cb(this.node);
}
}
class Vue {
constructor({el, data, methods, render}) {
this.$ele = document.querySelector(el);
// x
this.$dep = {};
this.$data = this._obs(data);
this.$methods = methods;
this._compileHtml(this.$ele);
}
// 数据劫持
_obs(data) {
let _that = this
return new Proxy(data, {
get(target, key) {
return target[key];
},
set(target, key, value) {
let val = Reflect.set(target, key, value);
_that.$dep[key].forEach(item => item.update());
return val;
}
});
}
// 订阅
_pushWatcher(watcher) {
if (!this.$dep[watcher.key]) {
this.$dep[watcher.key] = [];
}
this.$dep[watcher.key].push(watcher);
}
// 解析html
_compileHtml(ele) {
const nodes = Array.from(ele.children);
let data = this.$data;
for(let node of nodes) {
let attrs = Array.from(node.attributes);
// 判断是否input???
if (node.getAttribute('v-model')) {
const key = node.getAttribute('v-model');
let cb = () => {
node.value = this.$data[key];
}
cb();
this._pushWatcher(new Watcher(node, cb, key));
node.addEventListener('input', () => {
data[key] = node.value;
});
}
if (node.getAttribute('v-bind')) {
const key = node.getAttribute('v-bind');
let cb = () => {
node.innerHTML = this.$data[key];
}
cb();
this._pushWatcher(new Watcher(node, cb, key));
}
if (node.getAttribute('@click')) {
const key = node.getAttribute('@click');
node.addEventListener('click', () => {
this.$methods[key].call(this);
});
}
// 子元素递归
if (node.children && node.children.length) {
this._compileHtml(node);
}
}
}
}
// 使用
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
num: 0
},
methods: {
addNum() {
this.$data.num++
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
注意点:
- Vue在初始化组件数据(data、props、computed、methods、events、watch)时,发生在create时期(beforeCreate与created之间)
- render(渲染)触发的是Data的getter操作(保证视图中用到的数据改变才触发后续的重新渲染)
- Vue2.0的数据劫持
Object.defineProperty方法是无法监听Array变化的- 尤大使用了hack手法,重写了['push', 'pop', 'shift', 'unshift', 'splice', 'sort', 'reverse'],
- 同时使用
const arrayMethods = Object.create(arrayProto)确保不污染原生数组方法
# 异步更新 && NextTick
Vue的$nextTick的实现主要利用了JS的EventLoop
Vue为什么有$nextTick ?
- Vue的Dom更新操作是异步更新,调用
queueWatcher函数 - queueWatcher中,Watch对象并不是立即更新视图,而是
queue.push(watcher)(被push进了一个队列queue) - 更新的过程是异步的(微任务实现,如果浏览器不支持微任务则降级为setTimeout)
# $nextTick降级策略(由微任务降级到宏任务)
$nextTick方法内部有timerFunc函数
if (typeof Promise !== 'undefined' && isNative(Promise)) {
var p = Promise.resolve();
timerFunc = function () {
p.then(flushCallbacks);
//在有问题的UIWebViews中,Promise.then并没有完全破坏,但是
//它可能会陷入一种奇怪的状态,其中回调被推入
//微任务队列但是队列没有被刷新,直到浏览器
//需要做一些其他工作,例如处理计时器。因此我们可以
//通过添加空计时器“强制”刷新微任务队列。
if (isIOS) { setTimeout(noop); }
};
isUsingMicroTask = true;
} else if (!isIE && typeof MutationObserver !== 'undefined' && (
isNative(MutationObserver) ||
// PhantomJS 和 iOS 7.x
MutationObserver.toString() === '[object MutationObserverConstructor]'
)) {
// 当Promise不可用时,使用MutationObserver
// 例如PhantomJS,iOS7,Android 4.4
//(#6466 MutationObserver在IE11中不可靠)
var counter = 1;
var observer = new MutationObserver(flushCallbacks);
var textNode = document.createTextNode(String(counter));
observer.observe(textNode, {
characterData: true
});
timerFunc = function () {
counter = (counter + 1) % 2;
textNode.data = String(counter);
};
isUsingMicroTask = true;
} else if (typeof setImmediate !== 'undefined' && isNative(setImmediate)) {
// 尽管setImmediate是宏任务,但是比setTimeout更好
timerFunc = function () {
setImmediate(flushCallbacks);
};
} else {
// 最后降级为 setTimeout.
timerFunc = function () {
setTimeout(flushCallbacks, 0);
};
}
所以:$nextTick的降级顺序是
- Promise
- MutationObserver (copy源码来自 Vue.js v2.6.10)
- setImmediate
- setTimeout
ps1: 顾轶灵在知乎上(2017-11-12)说:Vue 的 nextTick 实现移除了 MutationObserver 的方式(兼容性原因),取而代之的是使用 MessageChannel。但是在源码中并没有看到(2019-05-05 v2.6.10)
ps2: 其实中途确实使用过 MessageChannel 但是出现了一些BUG,所以 尤大把代码回滚了
# 为什么$nextTick要降级 ?
根据HTML标准,在每个task运行完以后,UI都会重渲染,那么在microtask中就完成数据更新,当前 task 结束就可以得到最新的 UI 了。
- 如果新建一个 task 来做数据更新,那么渲染就会进行两次。
- 并且setTimeout的间隔时间比较久
# 为什么要异步更新 ?
和节流、防抖差不多吧。如果没有异步更新操作,那么连续的改动都会直接操作DOM更新视图,这是非常消耗性能的。(react 中会有一个说法:不在乎过程,只在乎结果)
而且queueWatcher中有watcher.id防重复
export function queueWatcher (watcher: Watcher) {
const id = watcher.id
// 检验id是否存在,已经存在则直接跳过
if (has[id] == null) {
has[id] = true
if (!flushing) {
// 如果没有flush,直接push到队列中
queue.push(watcher)
} else {
let i = queue.length - 1
while (i >= 0 && queue[i].id > watcher.id) {
i--
}
queue.splice(Math.max(i, index) + 1, 0, watcher)
}
if (!waiting) {
waiting = true
nextTick(flushSchedulerQueue)
}
}
}
# Diff算法
patch的核心是diff算法
diff算法是通过同层的树节点比较而非对树进行逐层搜索遍历,时间复杂度为O(n)
diff算法主要为2种:
- 值得比较(sameVnode)
- 不值得比较
判断两个VNode节点是否是同一个节点(sameVnode),需要满足以下条件
key相同tagName相同- isComment(是否为注释节点)相同
- 是否 data
- 当标签是
<input>的时候,type必须相同
源码如下:
function sameVnode (a, b) {
return (
a.key === b.key &&
a.tag === b.tag &&
a.isComment === b.isComment &&
isDef(a.data) === isDef(b.data) &&
sameInputType(a, b)
)
}
如果值得比较:
- 判断是否新老节点只有文本 -> 替换文本
- 新节点有子节点,老节点没有子节点 -> 清空老节点文本,为当前节点添加子节点
- 新节点没有子节点,老节点有子节点 -> 清空老节点的子节点
- 新老节点都有子节点:调用updateChildren方法
如果不值得比较,那么会移除旧的DOM,创建新的DOM
updateChildren方法源码如下:(遍历过程中这几个变量都向中间靠拢)
while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) {
if...
++oldStartIdx
++newStartIdx
if...
--oldEndIdx
--newEndIdx
}
Vue会逐级递归对children件进行diff,单每个组件的diff是独立的
# keep-alive
Vue中keep-alive是一个组件:
- 在create中创建cache对象
- 在destroyed时销毁cache
缓存的是Vnode的componentInstance(组件实例),而且在创建之初会getFirstComponentChild(this.$slots.default)
if (this.cache[key]) {
vnode.componentInstance = this.cache[key].componentInstance
} else {
this.cache[key] = vnode
}
include 和 exclude 属性允许组件有条件地缓存
// 允许使用字符串和正则
function matches (pattern: string | RegExp, name: string): boolean {
if (typeof pattern === 'string') {
return pattern.split(',').indexOf(name) > -1
} else if (isRegExp(pattern)) {
return pattern.test(name)
}
return false
}
并且会监视include和exclude,在被修改的时候对cache进行修正
watch: {
include (val: string | RegExp) {
pruneCache(this.cache, this._vnode, name => matches(val, name))
},
exclude (val: string | RegExp) {
pruneCache(this.cache, this._vnode, name => !matches(val, name))
}
},
keep-alive有2个新的生命周期activated和deactivated,在进入/退出时触发。
触发顺序:created-> mounted-> activated
# Vue 对Array的hack实现
Vue2 使用的数据劫持方式是无法劫持数组改变的,所以 Array 类型需要 Hack。
- 实现了个包含需要hack的数组方法的对象
- 在
Observer时将该hack方法覆盖需要劫持的Array的原型
var arrayProto = Array.prototype;
// 创建一个对象, 该对象以数组的原型为原型
var arrayMethods = Object.create(arrayProto);
// 实现的hack 方法
var methodsToPatch = [
'push',
'pop',
'shift',
'unshift',
'splice',
'sort',
'reverse'
];
methodsToPatch.forEach(function (method) {
// cache original method
// 获取到原生的 数组方法
var original = arrayProto[method];
/*
使 arrayMethods 获得了一个包含原生数组的方法
同时还获得了调用 观察者对象的 更新能力
后续在 观察者类<Observer> 中判断 是否 Array
如果是 Array 就会 调用 protoAugment<有__proto__情况> || copyAugment<无__proto__情况>
替换被监听的数组的 __proto__ 替换为 arrayMethods
*/
def(arrayMethods, method, function mutator () {
var args = [], len = arguments.length;
while ( len-- ) args[ len ] = arguments[ len ];
// 执行真正的方法
var result = original.apply(this, args);
var ob = this.__ob__;
var inserted;
switch (method) {
case 'push':
case 'unshift':
inserted = args;
break
case 'splice':
inserted = args.slice(2);
break
}
if (inserted) { ob.observeArray(inserted); }
// notify change
ob.dep.notify();
return result
});
});
//... 省略
var Observer = function Observer (value) {
this.value = value;
this.dep = new Dep();
this.vmCount = 0;
def(value, '__ob__', this);
// 对 Array进行 hack
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
if (hasProto) {
protoAugment(value, arrayMethods);
} else {
copyAugment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys);
}
this.observeArray(value);
} else {
this.walk(value);
}
};
//... 省略
// 有__proto__时 挂载__proto__
function protoAugment (target, src) {
/* eslint-disable no-proto */
target.__proto__ = src;
/* eslint-enable no-proto */
}
/**
* Augment a target Object or Array by defining
* hidden properties.
没有__proto__时
给对象每个属性都配一个对应方法
*/
/* istanbul ignore next */
function copyAugment (target, src, keys) {
for (var i = 0, l = keys.length; i < l; i++) {
var key = keys[i];
def(target, key, src[key]);
}
}
# Vuex源码实现
Vuex 的 install
- 通过
applyMixin(Vue)在Vue的beforeCreate时注入 - 为了获取同一份store,会尝试从
options.store(root节点)和options.parent.$store获取store
Vuex 双向绑定
// 一
// 通过 new Vue实现$$state的双向绑定
store._vm = new Vue({
data: {
$$state: state
},
computed: computed
});
// 二
// 当获取state时,返回以双向绑定的$$sate
var prototypeAccessors$1 = { state: { configurable: true } };
prototypeAccessors$1.state.get = function () {
return this._vm._data.$$state
};
// 三
// 将state定义在原型中
Object.defineProperties( Store.prototype, prototypeAccessors$1 );
vuex 单向修改 state 原理
在严格模式中:会调用store._vm.$watch(...),监听state的改动,如果!_committing则会抛出错误。
只能使用 mutation 更改state
_withCommit (fn) {
const committing = this._committing
this._committing = true
fn()
this._committing = committing
}
action是异步的,使用的是Promise。 - -没啥好说的。
# Vuex和Vue的冲突
见官网:Vuex表单处理
当在严格模式中使用 Vuex 时(修改state),在属于 Vuex 的 state 上使用 v-model 会比较棘手:
由于v-model修改是在Vue中修改的,但是在Vuex的store._vm.$watch(...)所监听中,this._committing并不是_committing
<input v-model="obj.message">
// 解决方案 一
<input :value="message" @input="updateMessage">
methods: {
updateMessage (e) {
this.$store.commit('updateMessage', e.target.value)
}
}
// 解决方案 二
<input v-model="message">
computed: {
message: {
get () {
return this.$store.state.obj.message
},
set (value) {
this.$store.commit('updateMessage', value)
}
}
}
# Vue 的计算属性
计算属性就是 data 数据劫持的进一步封装。
核心实现:
- 先实现
$data的双向绑定 - 调用computed对象的getter方法
- 触发 对应$data 的getter方法
- 将对应
$data的 观察者push到 computed对象的Watcher中
从 initComputed 方法开始源码分析:-> 源码来自(vue v2.6.10),不重要的内容省略。
function initComputed (vm, computed) {
var watchers = vm._computedWatchers = Object.create(null);
for (var key in computed) {
var userDef = computed[key];
var getter = typeof userDef === 'function' ? userDef : userDef.get;
// 异常部分 略...
watchers[key] = new Watcher(
vm,
getter || noop,
noop,
computedWatcherOptions
);
if (!(key in vm)) {
defineComputed(vm, key, userDef);
} else {
// 略...
}
}
}
在初始化计算属性时主要做了3件事情
- 遍历所有挂载的计算属性
- 通过
new Watcher监听每一个计算属性 - 调用
defineComputed方法
而上面的 defineComputed 主要是调用了 createComputedGetter 或 createGetterInvoker 方法
function defineComputed ( target, key, userDef ) {
if (typeof userDef === 'function') {
sharedPropertyDefinition.get = shouldCache
? createComputedGetter(key)
: createGetterInvoker(userDef);
sharedPropertyDefinition.set = noop;
}
// 略...
}
function createComputedGetter (key) {
return function computedGetter () {
var watcher = this._computedWatchers && this._computedWatchers[key];
if (watcher) {
if (watcher.dirty) {
// evaluate 其实时调用自身 get 方法
watcher.evaluate();
}
if (Dep.target) {
// 将自身push到Dep 中
watcher.depend();
}
return watcher.value
}
}
}
function createGetterInvoker(fn) {
return function computedGetter () {
return fn.call(this, this)
}
}
实现 computed 计算属性重点就在于 createComputedGetter 方法。在这个方法中,无非就是通过 watcher.evaluate(); 调用自身的 get 方法将内部所有用到的 this.xxx 全部加入到 Dep 中,从而统一监听内部用到的 this.xxx,这样计算属性就完成了。
# Vue.use 插件安装
// 首先会校验`installedPlugins`数组中是否已经含有对应组件
const installedPlugins = this._installedPlugins || (this._installedPlugins = [])
// 防止重复安装
if (installedPlugins.indexOf(plugin) > -1) {
return this
}
const args = toArray(arguments, 1)
// 插入Vue
args.unshift(this)
// 插件包含 install方法
if (typeof plugin.install === 'function') {
plugin.install.apply(plugin, args)
// 插件是函数
} else if (typeof plugin === 'function') {
plugin.apply(null, args)
}
// 缓存,用以检测是否重复安装
installedPlugins.push(plugin)
return this
# VueRouter 实现
VueRouter 实际上是一个 Vue的插件,通过
Vue.use(VueRouter)来调用VueRouter的install方法
hash 路由通过 监听 hashchange 形成堆栈实现
<ul>
<li onclick="router.push('/')">首页</li>
<li onclick="router.push('/aa')">AA</li>
<li onclick="router.push('/bb')">BB</li>
</ul>
<div id="routerView"></div>
<script>
var routerView = document.getElementById("routerView");
class HashRouter {
constructor({routes}) {
this.routes = routes || [];
this.addListener();
}
push(url) {
const href = "#" + url;
window.location.href = href;
}
router() {
const curUrl = window.location.hash.slice(1) || '/';
// 找到路由
const route = this.routes.find(r => r.path === curUrl);
// 简单的校验下异常
if (typeof route === 'object') {
routerView.innerHTML = route.component;
}
}
addListener() {
// 监听load事件,防止刷新页面数据丢失
window.addEventListener("load", this.router.bind(this));
window.addEventListener("hashchange", this.router.bind(this))
}
}
//初始化 使用
var router = new HashRouter({
routes: [{
path: '/',
component: '<div>这里是 根</div>'
},
{
path: '/aa',
component: '<div>这里是 AA</div>'
},
{
path: '/bb',
component: '<div>这里是 BB</div>'
}
]
});
</script>
当然也可以使用 history 模式,原理大部分都是一样的
- 通过
popstate监听history的改变 - 通过
window.history.pushState({}, null, url);推入堆栈
- 小细节:
popstate并不能监听pushState的改变 - 故:需主动触发
router
<ul>
<li onclick="router.push('/')">首页</li>
<li onclick="router.push('/aa')">AA</li>
<li onclick="router.push('/bb')">BB</li>
</ul>
<div id="routerView"></div>
<script>
var routerView = document.getElementById("routerView");
class HistoryRouter {
constructor({routes}) {
this.routes = routes || [];
this.addListener();
}
push(url) {
window.history.pushState({}, null, url);
// pushState 并不会触发 popstate,所以需要主动触发 router
this.router();
}
router() {
const curUrl = window.location.pathname;
// 找到路由
const route = this.routes.find(r => r.path === curUrl);
console.log(route, curUrl)
// 简单的校验下异常
if (typeof route === 'object') {
routerView.innerHTML = route.component;
}
}
addListener() {
// 监听load事件,防止刷新页面数据丢失
window.addEventListener("load", this.router.bind(this));
window.addEventListener("popstate", this.router.bind(this))
}
}
//初始化 使用
var router = new HistoryRouter({
routes: [{
path: '/',
component: '<div>这里是 根</div>'
},
{
path: '/aa',
component: '<div>这里是 AA</div>'
},
{
path: '/bb',
component: '<div>这里是 BB</div>'
}
]
});
</script>
实现总结:
- 通过
Vue.mixin在beforeCreate中初始化router - 全局注册2个组件:
router-link和router-view
router-link组件:就是上例的<li onclick="router.push('/')">首页</li>router-view组件:就是上例的<div id="routerView"></div>
注入:
// 通过 Vue.mixin 在 beforeCreate 中注入
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
// 判断组件是否存在 router 对象,该对象只在根组件上有
if (isDef(this.$options.router)) {
// 根路由设置为自己
this._routerRoot = this
this._router = this.$options.router
// 初始化路由
this._router.init(this)
// 很重要,为 _route 属性实现双向绑定
// 触发组件渲染
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '_route', this._router.history.current)
} else {
// 用于 router-view 层级判断
this._routerRoot = (this.$parent && this.$parent._routerRoot) || this
}
registerInstance(this, this)
},
destroyed() {
registerInstance(this)
}
})
// 全局注册组件 router-link 和 router-view
Vue.component('RouterView', View)
Vue.component('RouterLink', Link)
← Fiber 源码解析 React 简况 →
